Introduction
The 1929 Great Depression, one of history’s most significant economic downturns, changed the world in ways that are still felt today. Its ripple effects shaped economic policies, financial systems, and global trade frameworks that govern the modern economy. Let’s explore how this historic event continues to influence our lives.
Historical Background
The Great Depression began with the stock market crash of October 1929, wiping out billions in wealth overnight. By the early 1930s, unemployment in the United States soared to 25%, and global economies entered a downward spiral. The resulting economic collapse forced governments to rethink the foundations of capitalism and economic regulation.
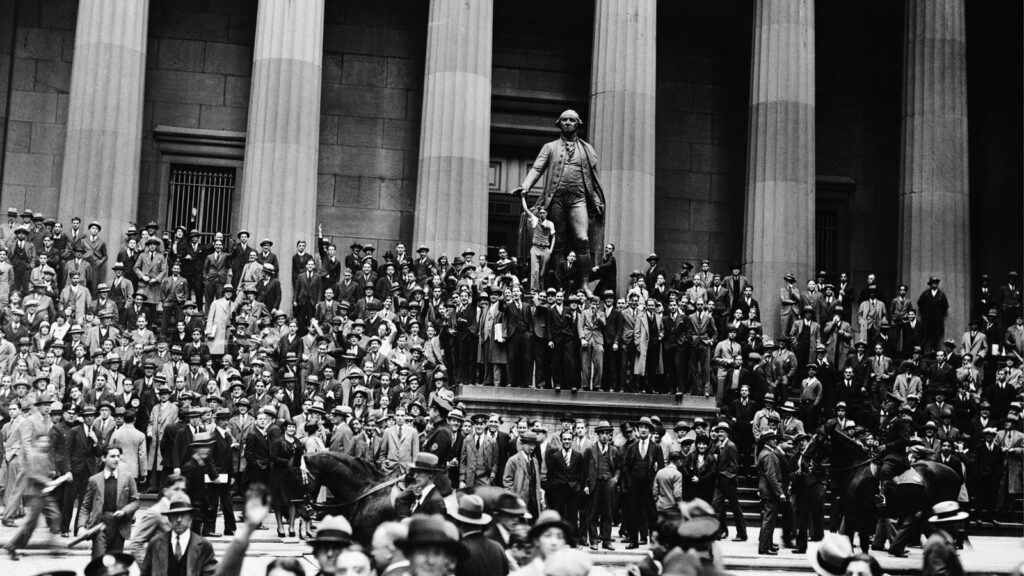

New York on the day wall street crashed
Economic Analysis
Causes
The Depression resulted from a mix of speculative stock market behavior, excessive bank lending, and weak regulatory frameworks. It exposed the dangers of unchecked financial speculation and reliance on credit.
Events
Bank failures spread fear, halting investments and consumer spending. As demand plummeted, industries collapsed, leaving millions jobless. International trade slowed due to protectionist policies like the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act.
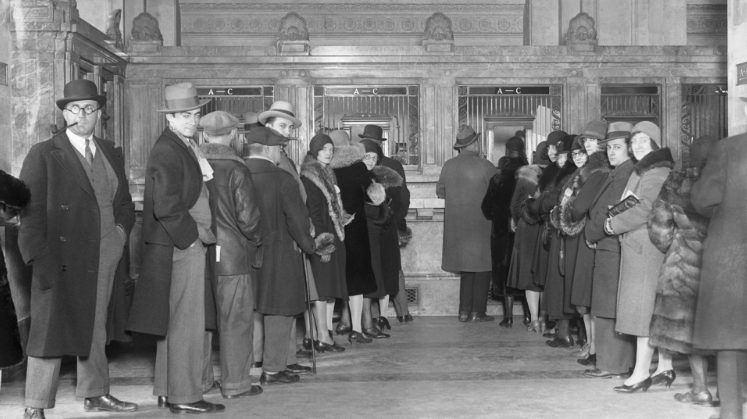

people lining up outside a bank during the Great Depression
Aftermath
The crisis led to the creation of safety nets, including unemployment insurance and welfare programs. Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal introduced reforms like Social Security and labor protections, reshaping the role of government in economic affairs.
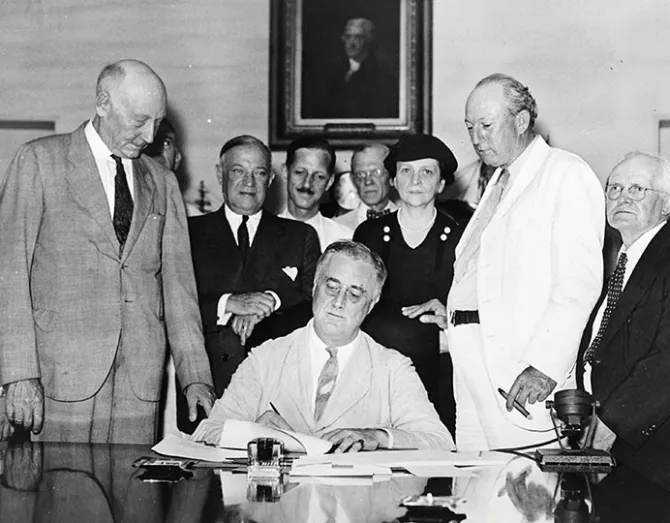

The New Deal in New Yok City
Long-term Effects
- Keynesian Economics: The Depression paved the way for John Maynard Keynes’ ideas on government intervention, which remain central to modern fiscal policy.
- Financial Regulation: Institutions like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) emerged to prevent future collapses.
How It Affects Us Today
- Government Intervention: During crises like the 2008 financial meltdown and the COVID-19 pandemic, governments applied lessons from 1929 to stabilize economies through stimulus packages and bailouts.
- Unemployment Policies: The labor protections and social safety nets initiated in the 1930s continue to safeguard workers during economic downturns.
- Global Trade: The interdependence of modern economies echoes the lessons of 1929: protectionism harms everyone. Efforts like the World Trade Organization (WTO) aim to foster cooperation, avoiding a repeat of trade wars.
- Banking Oversight: The Depression’s legacy includes stricter financial regulations and central bank policies aimed at ensuring stability and avoiding systemic risks.
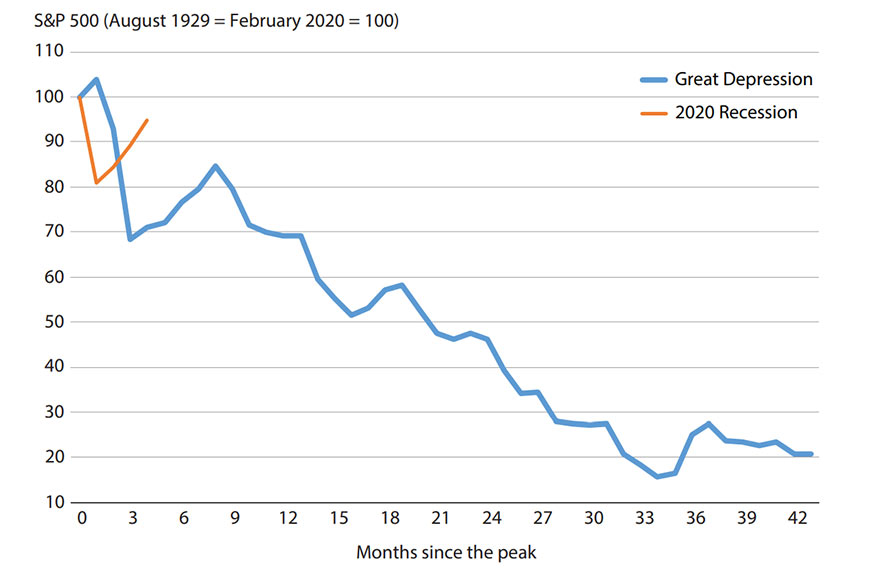
The S&P 500 (Standard and Poor’s stock price index) in 1929 and 2020
Conclusion
The 1929 Great Depression reshaped the global economy and laid the foundation for today’s economic systems. Its lessons remind us of the importance of regulation, global cooperation, and resilience in times of crisis. To understand today’s financial world, we must remember how the past continues to guide us.
